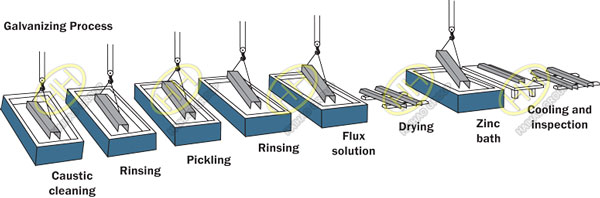
Process of hot-dip galvanized
Hot dip galvanizing is the process of galvanizing coated materials such as steel, iron, or aluminum to prevent them from corroding due to possible exposure to harsh conditions.Hot dip galvanizing is to dip the workpiece in a solution of zinc.This causes a metallurgical reaction that combines the outer layers of both metals, creating a uniform and highly resistant surface.
Formation layer is a galvanized iron matrix between the outermost pure zinc layer and form an iron – during the zinc alloy.
Model of the Hot Dip Galvanizing Process
The workpiece surface is formed during hot-dip coating of iron – zinc alloy layer, which makes it between the pure zinc layer and the iron Good combination, the process can be simply described.
As follows: when an iron workpiece is immersed in molten zinc liquid, zinc and α iron ( body-centered ) solid solution is first formed at the interface.

Hot galvanized Grade 2 Bolts and nuts finished in Haihao Group
This is a crystal formed by dissolving zinc atoms in the solid state of the base metal iron. The two metal atoms are fused and the attraction between the atoms is relatively small. Therefore, when zinc reaches saturation in the solid solution, the two elemental atoms of zinc and iron diffuse with each other, and the zinc atoms diffused ( or infiltrated ) into the iron matrix migrate in the matrix of the matrix, gradually form an alloy with iron, and diffuse The iron in the molten zinc solution forms an intermetallic compound FeZn13 with zinc , which sinks into the bottom of the hot-dip galvanizing pot, which is zinc slag. When the workpiece is removed from the zinc bath, a pure zinc layer is formed on the surface, which is a hexagonal crystal. Its iron content is not more than 0.003%.
Haihao group provide professional service and products,we work with many international projects.If you have related inquiry,pls contact us :sales@haihaogroup.com

