Introduction of forging process
Forging is the most commonly used process for pipeline products.When forging,an initially simple part, the billet, is plastically deformed between the two dies to obtain the desired final shape.In order to better understand and optimize the forging process, it is necessary to classify it systematically.There are a large number of forging processes can be divided into the following:

Large Size Forged Blind Flanges Under Production
1. According to the temperature
According to the temperature,the forging process can be divided into cold forging,warm forging and hot forging.
What is cold forging?
Forging is carried out at or near room temperature (below the recrystallization temp) of the metal.Carbon and standard alloy steels are most commonly cold-forged.Cold forging is generally preferred when a metal, such as aluminium, has become soft.This process is generally cheaper than hot forging and the final product requires little or no finishing work. Cold forging is also less susceptible to contamination problems, and the final component features a better overall surface finish.
Advantages of cold forging: Production rates are very high with exceptional die life,improve the mechanical performance, less friction between die surface and work piece, easy lubrication, no oxidation or scaling on the work.
Residual stresses can occur, heavier and more powerful equipment is needed, more powerful tools are needed, and tool design and manufacturing are critical.
Disadvantages of cold forging: Residual stress may occur,heavier and more powerful equipment is needed,more powerful tools are needed,tool design and manufacturing are critical.
What is warm forging?
The temperature range for the warm forging of steel runs from above room temperature to below the recrystallization temperature.Compared with cold forging, warm forging has the potential advantages of:Reduced tooling loads,reduced press loads, increased steel ductility, elimination of need to anneal prior to forging, and favorable as-forged properties that can eliminate heat treatment.In warm forging, the billet is heated below the recrystallization temperature, up to 700 to 800 0C for steels, in order to lower the flow stress and the forging pressures.
Advantages of warm forging:High production rates,excellent dimensional tolerances and surface finish for forged parts,significant savings in material and machining,favorable grain flow to improve strength,greater toughness of the forged part.
What is hot forging?
Hot forging is the most widely used process.Forging is carried out at a temperature above the recrystallization temperature of the metal.The recrystallization temperature is defined as the temperature at which the new grains are formed in the metal. This kind of extreme heat is necessary in avoiding strain hardening of the metal during deformation.
Advantages of hot forging: High strain rates and hence easy flow of the metal,recrystallization and recovery are possible, forces required are less.
Disadvantages of hot forging: Lubrication is difficult at high temperatures, oxidation and scaling occur on the work piece, poor surface finish, less precise tolerances, possible warping of the materialduring the cooling process.
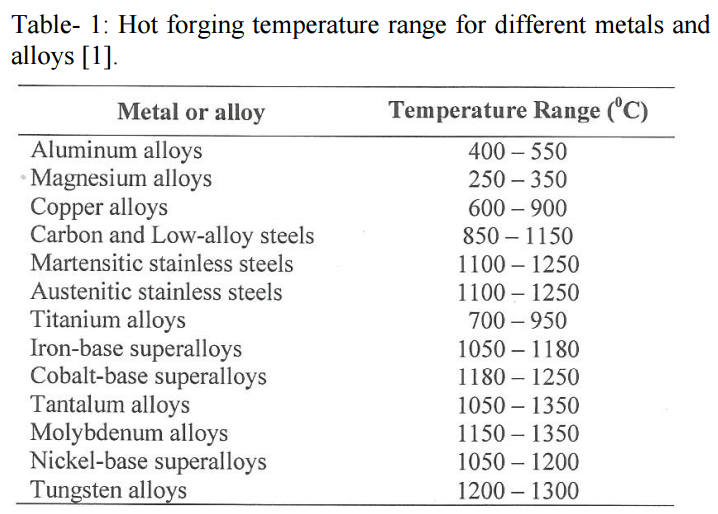
Hot forging temperature range for different metals and alloys
2.Types according to arrangements of dies
According to arrangements of dies forging processes can be divided into open-die forging, closed die forging.
What is open die forging?
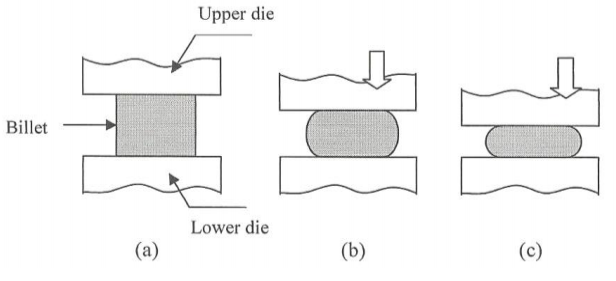
open die forging
Forging in which the flat dies of simple shape are used to allow the material to freely deformed in lateral directions of applied load.Open die forging is only suitable for simple shapes for its less dimensional accuracy, there is high requires on the skill of operators, the dies of open die forgings are simple and cheap, which is simplest of all the forging operations.
What is closed die forging?
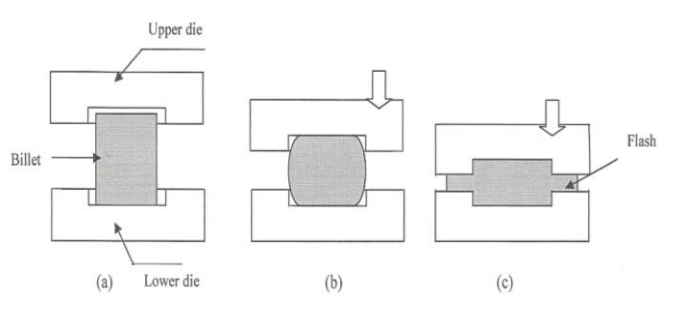
closed die forging
Closed-die forging is also known as impression die forging.Forging in which the material is fully constrained in the cavity created by the upper and lower die halves. It allows for more accurate forming of parts, requires higher interfacial pressure and very precise control of material volume and correct mold design.Closed-die forging is a form of impression-die forging,which does not depend on flash formation to achieve complete filling of the die. Material is deformed in a cavity that allows little or no escape of excess material, thus placing greater demands on die design.
Work is rough forged close to final shape by blocking die, work is forged to final shape and dimensions by finishing die, both blocking die and finishing die are machined into the same die block, more number of dies are required depending on the complexity of the job, two die halves close-in and work is deformed under high pressure,high dimensional accuracy/close control on tolerances, suitable for complex shapes, dies are complex and more expensive,large production rates are necessary to justify high costs.
It allows for more accurate forming of parts, requires higher interfacial pressure and very precise control of material volume and correct mold design.Closed die forging is a form of stamping die forging, which does not rely on the formation of burr to complete the filling of the die.Material deformation in the cavity, so that the excess material almost or no escape, so the mold design put forward higher requirements.Characteristics: work is the rough forging close to the final shape by blocking the death, the final work is forged mold of shapes and sizes and prevent death and complete mould processing into the same module, need more the number of death depends on the complexity of the work, two half dead melee is deformed under the high pressure of work, high dimensional accuracy/close control of tolerance, suitable for complex shape, mold is complicated and expensive, large production speed is necessary, to prove that the high cost.
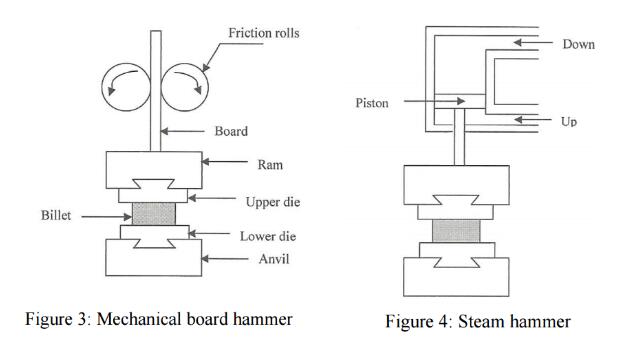
Mechanical board hammer and steam hammer
3.Types according to forging equipment
Forged components are shaped either by a hammer or press. Forging on the hammer is carried out in a succession of die impressions using repeated blows. The quality of the forging,and the economy and productivity of the hammer process depend upon the tooling and the skill of the operator. In press forging, the stock is usually hit only once in each die impression and the design of each impression becomes more important while operator skill is less critical. The continuous development of forging technology requires a sound and fundamental understanding of equipment capabilities and characteristics. The equipment i.e. presses and hammers used in forging, influences the forging process, since it affects the deformation rate and temperature conditions, and it determines the rate of production. The requirements of a given forging process must be compatible with the load, energy, time, and accuracy characteristics of a given forging machine.
Hammer forging
The most common type of forging equipment is the hammer and anvil. The hammer is the least expensive and most versatile type of equipment for generating load and energy to carry out a forging process. This technology is characterized by multiple impact blows between contoured dies. Hammers are primarily used for hot forging. There are basically two types of anvil hammers: Gravity-drop hammers and power drop hammers. In a simple gravity-drop hammer, the upper ram is connected to a board (board-drop hammer), a belt (belt-drop hammer), a chain (chain-drop hammer),or a piston (oil-, air-, or steam-lift drop hammer).The ram is lifted to a certain height and then dropped on the stock placed on the anvil. During the down stroke, the ram is accelerated by gravity and builds up the blow energy. The upstroke takes place immediately after the blow. The operation principle of a power-drop hammer is similar to that of an air-drop hammer. In the down stroke, in addition to gravity,the ram is accelerated by steam, cold air, or hot air pressure. In the power-drop hammer, the acceleration of the ram is enhanced with air pressure applied on the top side of the ram cylinder. Figure 3 shows mechanical board hammer- It is a stroke restricted machine. Repeatedly the board (weight) is raised by friction rolls and is dropped on the die. Its rating is in the terms of weight of the ram and energy delivered. Figure 4 shows steam hammer- It uses steam in a piston and cylinder arrangement. It has greater forging capacity. It can produce forgings ranging from a few kg to several tones. It is preferred in closed-die forging.
Press forging
In press forging, the metal is shaped not by means of a series of blows as in hammer forging, but by means of a single continuous squeezing action. There are two main types:mechanical and hydraulic presses. Mechanical presses function by using cams, cranks and/or toggles to produce a preset (a predetermined force at a certain location in the stroke) and reproducible stroke. Due to the nature of this type of system,different forces are available at different stroke positions. Mechanical presses are faster than their hydraulic counterparts (up to 50 strokes per minute). Their capacities range from 3 to 160 MN (300 to 18,000 short tons-force). Hydraulic presses use fluid pressure and a piston to generate force. Figure 5 shows hydraulic press.It is a load restricted machine. It has more of squeezing action than hammering action. Hence dies can be smaller and have longer life than with a hammer. Features of
Hydraulic Press
Full press load is available during the full stroke of the ram, ram velocity can be controlled and varied during the stroke, it is a slow speed machine and hence has longer contact time and hence higher die temperatures, the slow squeezing action gives close tolerance on forgings, initial cost is higher compared to hammers. The advantages of a hydraulic press over a mechanical press are its flexibility and greater capacity. The disadvantages include a slower, larger, and costlier machine to operate.
Haihao Group manufacture forged pipe fittings,forged flanges and butt welding pipe fittings,steel pipes in different dimensions,materials and standards.If you want to know more about our pipeline products,please email us:sales@haihaogroup.com

